Render Controls - Water¶
The
-
Still water: Changes whether waves are on the surface of the water.
-
Water visibility: Changes the distance that rays can travel through water before being terminated. Positive values beyond the range of the slider can be entered into the associated input field.
-
Water opacity: Changes the opacity of the surface of the water.
-
Use custom water color: Disables biome tinting for water and sets the water color to a custom color.
-
Pick color: Opens a color selector dialog box to change the color of the water. This control is only effective if Use custom water color is enabled.
-
Save as defaults: Saves the current water settings as the default water settings for new scenes.
Water World Mode Controls¶
-
Water world mode: Changes whether an infinite water plane is present in the scene.
-
Water height: Changes the altitude of the water in the Y-axis. Values beyond the range of the slider can be entered into the associated input field.
-
Lower water by Minecraft offset: Changes whether the altitude of the water plane is decreased by the distance between block level and in-game water level.
-
Hide the water plane in loaded chunks: Changes whether the water plane is visible within loaded chunks.
Procedural Water Controls¶
-
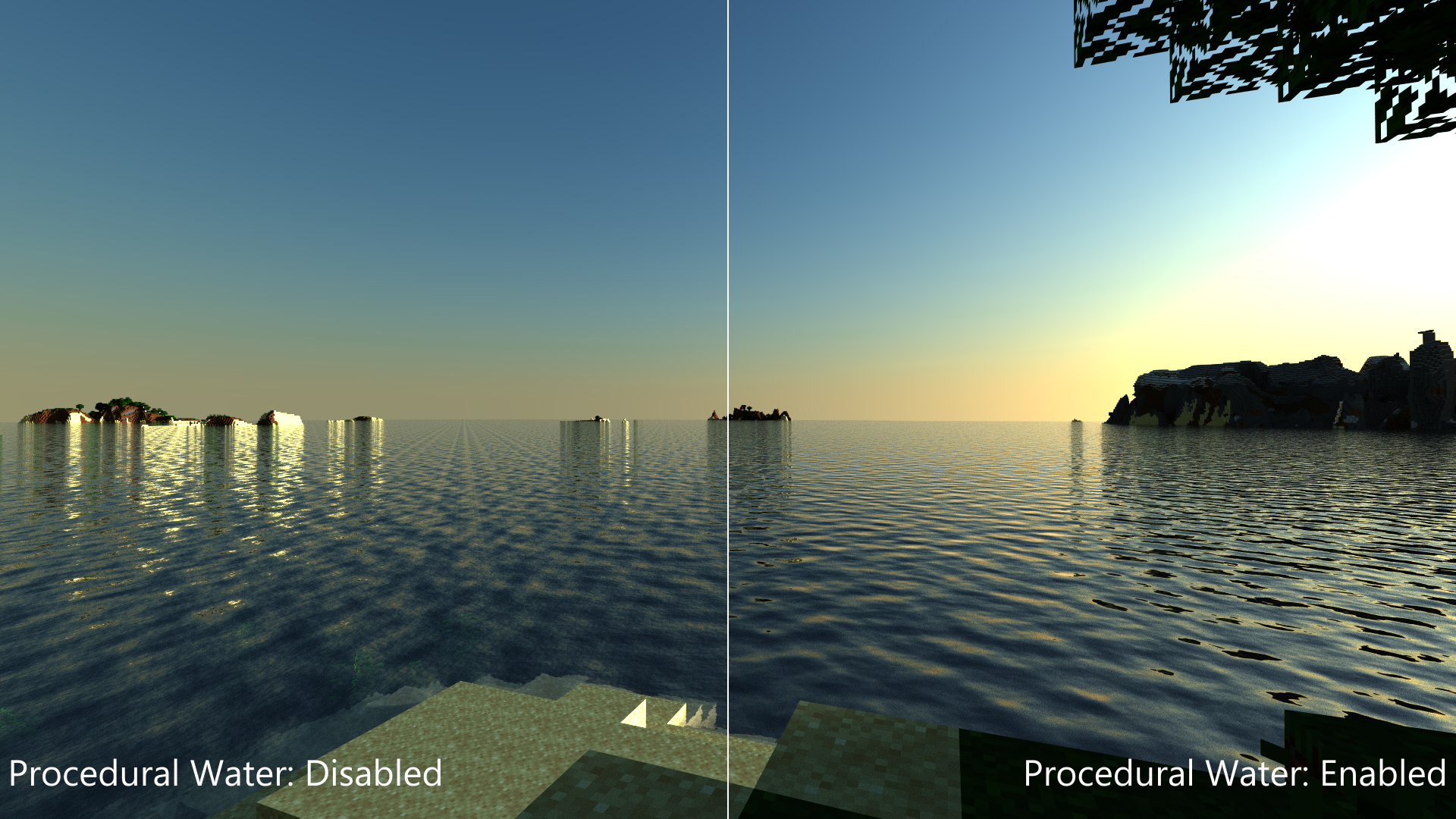
Procedural water: Changes whether configurable simplex noise is used to procedurally shade the water. See Figure 2 for a comparison between normal water and procedural water.
-
Iterations: Changes the number of iterations of noise used. Greater values add more detail to the waves, but decrease the rendering performance. Positive values beyond the range of the slider can be entered into the associated input field.
-
Frequency: Changes the frequency of noise used. Greater values shrink the waves horizontally while smaller values stretch the waves horizontally. Positive values beyond the range of the slider can be entered into the associated input field.
-
Amplitude: Changes the amplitude of noise used. Greater values stretch the waves vertically, while smaller values shrink the waves vertically. This only changes the apparent height of the waves; the water actually remains flat. Positive values beyond the range of the slider can be entered into the associated input field.
-
Animation speed: Changes the water appearance based on the Current animation time.
-